Autoimmune diseases develop when the immune system, which is meant to defend the body from infections, mistakenly targets healthy cells and tissues. This internal confusion can affect almost any part of the body, including the joints, skin, digestive system, thyroid, or nervous system. As a result, people may experience ongoing fatigue, pain, inflammation, brain fog, or recurring illness that does not seem to have a clear cause. Symptoms often appear gradually and can change over time, making them easy to dismiss or misdiagnose in the early stages.
Living with an autoimmune condition can be physically and emotionally challenging, especially because there is rarely a quick or simple fix. Genetics, environmental triggers, stress, infections, and lifestyle factors can all contribute to the development of these conditions. While most autoimmune diseases cannot be cured, they can often be managed effectively through medication, nutrition, stress management, and regular medical care. With the right support system and a better understanding of their condition, many people are able to adapt, regain control, and lead fulfilling, active lives despite the challenges.
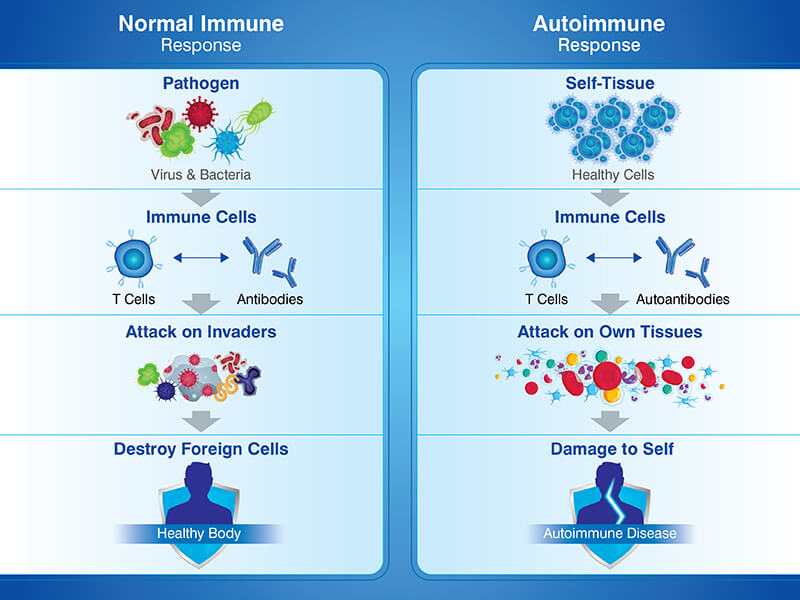
Individuals with an autoimmune disorder have a misdirected immune response which results in damage to their body’s cells, tissues and organs. The immune system sometimes attacks the body’s own cells or tissues.
During an appropriate immune response the antibodies initially neutralise pathogens but then get destroyed. In conditions involving autoimmunity the body fails to switch off the immune response. The condition leads to chronic inflammation, and this in turn can result in damage to tissues, and in addition to this, pain. It affects the skin, nerves, the body, joints or organs.
According to global health studies, autoimmune diseases affect 5–8% of the world’s population, with women accounting for nearly 75% of diagnosed cases.
There are more people suffering from autoimmune disorders than you might have believed. There are worldwide more than eighty distinct diseases brought on by the body’s immune response. In India, the number of such diseases is increasing.
Autoimmune conditions are rising worldwide. Currently, autoimmune conditions affect 1 in 10 individuals globally. According to the National Family Health Survey (NFHS), the prevalence of thyroid disorders among Indian women rose from 2.2% in NFHS-IV (2015-2016) to 2.9 % in NFHS-V (2020-2021), marking a notable increase within just five years.
A 2024 study in Uttar Pradesh reported rheumatoid arthritis to be three times more prevalent in urban areas than rural areas.
Source: orfonline.org
There’s no single cause, but here’s what we know from science and real-world clinical experience:
Care is often delayed because in rural India, people are not aware of specialist services and also there is a lack of access to these specialists. People in cities often experience hectic lifestyles, and a healthcare system which is disjointed can result in a misdiagnosis or a delay in appropriate treatment.
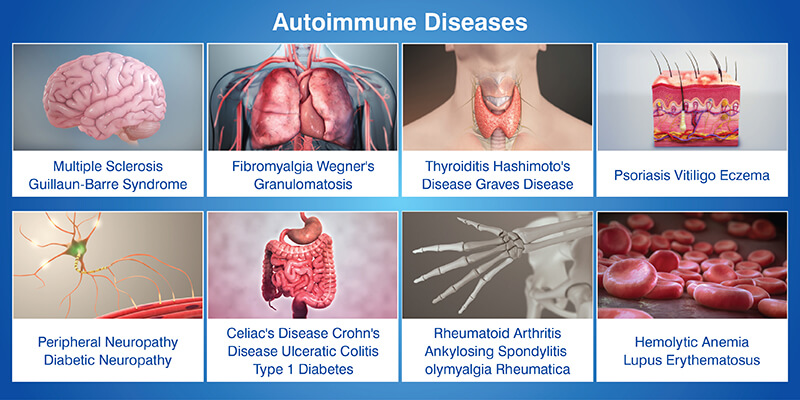
There are over 80 identified autoimmune conditions, ranging from organ-specific to systemic diseases that affect the whole body. Here are a few examples of autoimmune diseases.
The symptoms of many of these disorders tend to be somewhat non-specific, can also be found in numerous other conditions and can sometimes be and gone in attacks or flare-ups.
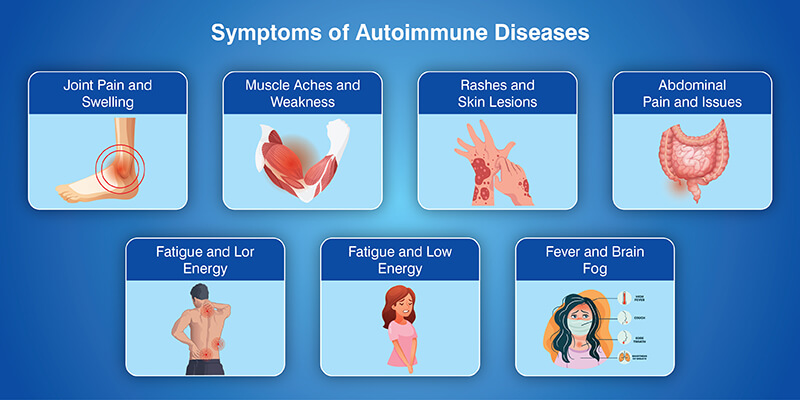
Symptoms vary widely depending on which part of the body is affected. Some people experience mild symptoms, while others face progressive disability if left untreated.
Early symptoms are often dismissed as stress or aging, which delays diagnosis and treatment.
Autoimmune diseases are frequently misdiagnosed because their causes are not singular in nature. Most evidence suggests that the cause of these conditions is a combination of several factors as opposed to a single trigger.
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can be challenging because symptoms often overlap with other conditions and develop gradually. Many patients experience months or even years of unexplained symptoms before receiving an accurate diagnosis.
Why diagnosis can take years: Early autoimmune symptoms may come and go, and lab results can appear normal in the initial stages. Inflammation is not always visible right away, which can lead to delayed specialist referrals or misdiagnosis.
Role of blood tests and imaging: Blood tests help detect inflammation markers and autoantibodies, but no single test can confirm most autoimmune diseases. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds help identify inflammation, joint damage, or organ involvement that blood tests may miss.
Importance of clinical history and symptom tracking: A detailed medical history and consistent symptom tracking help doctors recognize disease patterns over time. Patient-reported symptoms often provide crucial insights that tests alone cannot.
Why self-advocacy is important: Self-advocacy helps ensure symptoms are taken seriously. Asking questions, seeking second opinions, and clearly sharing symptom changes can lead to earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.
Modern medicine offers effective ways to control symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve daily functioning.
The most effective approach to the treatment of autoimmune diseases is personalized care, guided by a specialist and adjusted over time.
Living with an autoimmune disease often involves adjusting to ongoing physical and emotional challenges, especially as symptoms shift between flare-ups and remission. These conditions can influence many aspects of daily life, making support and adaptability essential.
Patient care may significantly involve the patient’s family. Families can affect a patient’s mental health. In many cases family life affects a patient’s physical health too. The person providing support can offer a non-judgmental ear, help out during periods of illness, encourage the sufferer to keep up with their doctor’s appointments and take it easy when the person’s energy levels are low or their capabilities are limited.
Those who are ill find much benefit from joining patient support groups where they can interact with others who are in similar situations. By being with others who are going through similar experiences, patients are supported, learn ways to cope, gain valuable insights from others who have been in their shoes and find people who understand them.
The healing that results from home and the community can be similar to that brought about by medicine.
Autoimmune diseases affect women more often due to hormonal influences, genetic factors, and differences in immune system functioning. Fluctuations in hormones such as estrogen are believed to play a role in immune regulation.
Autoimmune diseases can run in families, but inheriting a gene does not guarantee developing the condition. Genetics combined with environmental and lifestyle factors usually determine disease onset.
If symptoms continue despite normal test results, it is important to track symptoms, seek specialist care, and advocate for further evaluation. Many autoimmune diseases require ongoing observation before they can be diagnosed.
Support groups provide emotional support, shared experiences, practical coping strategies, and a sense of belonging. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can reduce isolation and improve mental well-being.
Yes, lifestyle changes such as balanced nutrition, regular low-impact exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep can help reduce flare-ups and improve overall quality of life when combined with medical treatment.
Those with an autoimmune disease have a chronic condition which they will live with for the rest of their lives. Nevertheless, their condition does not determine their life prospects or quality. People with the condition are able to lead full and active lives with the correct treatment and regular support.
Being aware of the causes of autoimmune disorders and how they are defined is vital for those who have them and their loved ones. Understanding the signs and symptoms of autoimmune diseases and the various treatments available is empowering.
When one becomes aware of mental health issues they can seek treatment promptly, which is key to making a full recovery. The journey towards recovery is easier when there is community support.